Knee Meniscus Repair
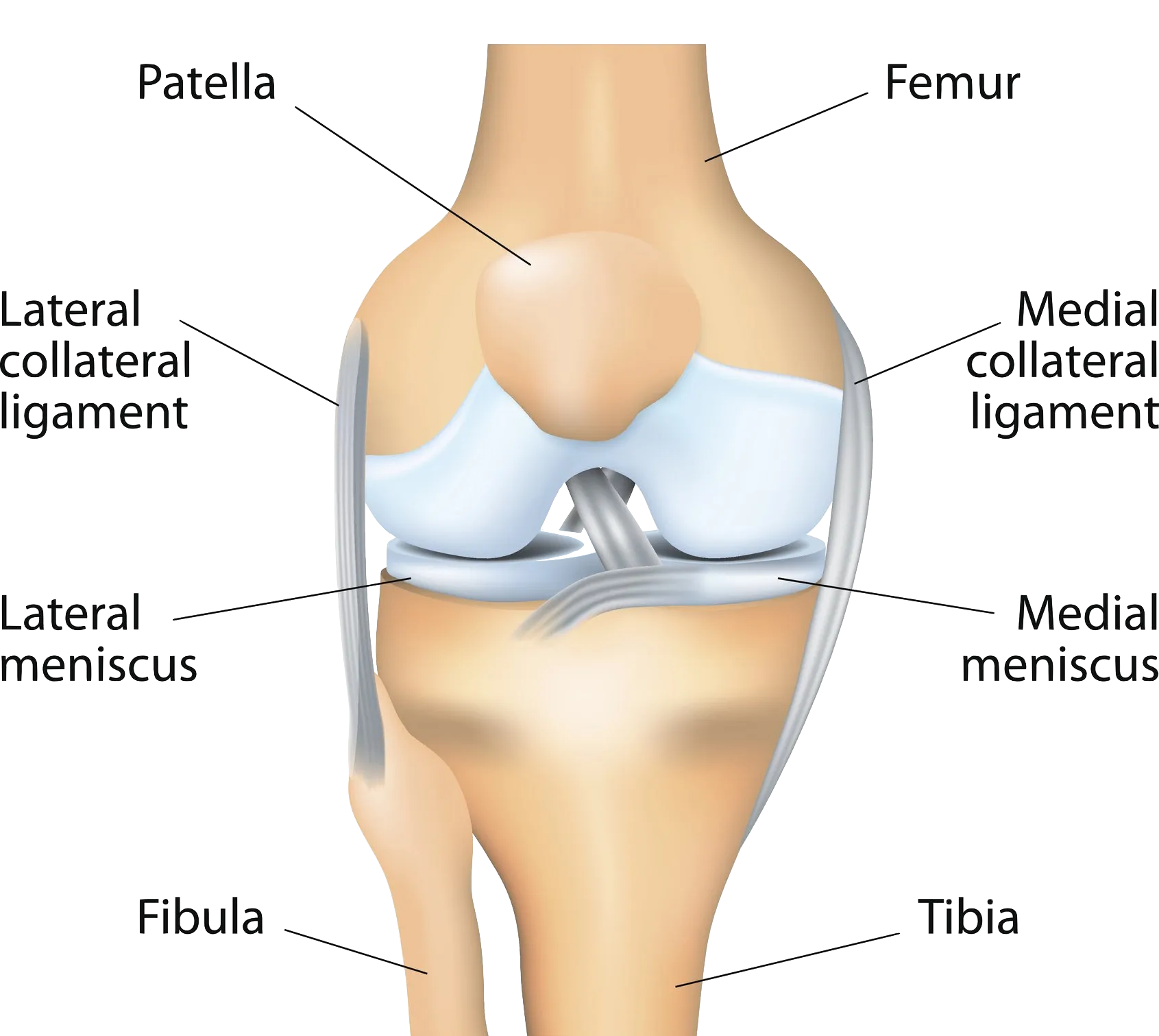
What is the Meniscus?
Each of your knees has two C-shaped pieces of menisci (cartilages) on the
- inner side (medial meniscus)
- outer side (lateral meniscus).
The meniscus is a crescent-shaped piece of fibro-cartilage that acts as a shock absorber between the thigh bone (femur) and the shin bone (tibia). The meniscus’ role is to:
- Reduce Wear,
- Protect Against Arthritis,
- Assist With The Stability Of The Knee Joint, and
- Help Disperse Fluid Around The Knee Joint Effectively.
The meniscus is an essential structure of the knee, and damage to the meniscus can lead to knee cartilage wear/osteoarthritis in the long term.
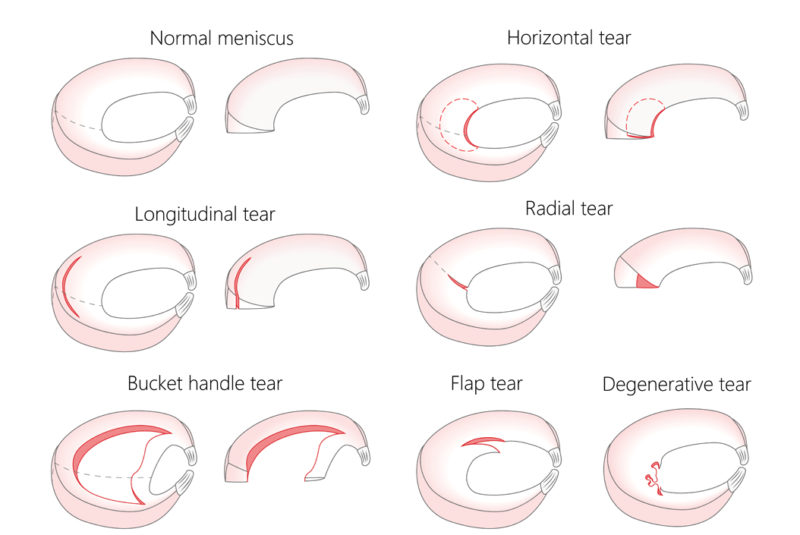
What is a Knee Meniscal Tear?
A Meniscal Tear is a break in your knee's meniscus wedge (cartilage).
Meniscal tears are common cartilage injuries in both contact and non-contact sports that require jumping quick lateral movements (e.g. netball).
Meniscus tears can be painful and debilitating.
A torn meniscus causes pain, swelling and stiffness. You also might feel a block to knee motion and have trouble extending your knee fully.
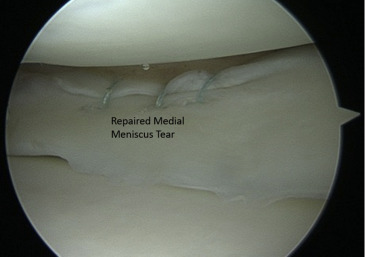
What is Knee Meniscus Repair?
Knee meniscus repair is a surgical procedure that aims to preserve the meniscus, and special devices are employed to deliver stitches to the tear until the meniscus heals.
Who is Suitable for Knee Meniscus Repair?
Not everyone with a meniscus tear requires surgery. Sometimes, non-surgical treatments such as rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE) and physical therapy can help alleviate symptoms. However, knee meniscus repair may be recommended if the tear is large or if non-surgical treatments are ineffective.
Suitable candidates for knee meniscus repair include:
- Patients with a torn meniscus that causes pain, clicking, and difficulty moving the knee
- Patients with a healthy knee ligament and stable knee joint
- Patients who are willing to undergo rehabilitation after surgery
- Adequate tear shape, size and location
- Younger age (less than 45 years old)
- Non-smokers
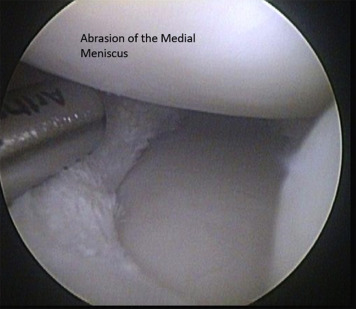
What happens if the meniscus tear is not repairable?
Your surgeon, intra-operatively, will judge the repairability of a meniscus tear. Extensive, chronic and complex tears are frequently not repairable. In these cases, your surgeon will perform a minimally invasive meniscus debridement using an arthroscopic shaver, removing only the tear and leaving the normal remaining meniscus in place.
What are the Benefits of Knee Meniscus Repair?
Knee meniscus repair offers several benefits, including
- Pain relief: Repairing the meniscus can reduce or eliminate knee pain.
- Improved knee function: A repaired meniscus can improve knee stability and range of motion, allowing patients to perform daily activities without difficulty.
- Better long-term outcomes: Knee meniscus repair has been shown to have better long-term outcomes than meniscectomy, delaying the development of chondropathy/osteoarthritis in the knee joint.
What are the Types of Knee Meniscus Repair?
Nowadays, all meniscus surgery is performed arthroscopically, a minimally invasive procedure done through small incisions in the knee using a tiny camera and surgical instruments. The surgeon will reposition the torn meniscus and use sutures or anchors to hold it in place while it heals.
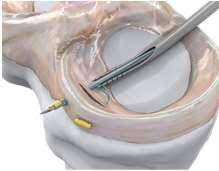
Knee Meniscus Repair Procedure
This surgery is typically performed under general anaesthesia and takes about half an hour to be completed.
Before the Procedure
- The surgeon will order diagnostic tests, such as an MRI, to evaluate the extent of the damage and determine the best course of treatment.
- The patient will be advised to refrain from eating or drinking for several hours before the procedure to avoid complications during anaesthesia.
- The patient may need to stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners, before the surgery.
During the Procedure
- The patient is given anaesthesia to make them comfortable and prevent pain during the surgery. The type of anaesthesia used may vary depending on the surgeon's preference and the patient's medical condition.
- The surgeon makes a small incision in the knee and inserts an arthroscope, a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light attached. This allows the surgeon to visualise the inside of the knee joint on a monitor.
- The surgeon examines the torn meniscus to determine the extent of the injury and decide whether to repair or debride it. If the tear is small and located in an area with a good blood supply, the surgeon may choose to repair it. If the tear is large, complex, or located in an area with poor blood supply, the surgeon may choose to remove the damaged part of the meniscus.
- If the decision is made to repair the meniscus, the surgeon will use small surgical instruments inserted through additional incisions in the knee to stitch the torn edges of the meniscus together. The stitches may be absorbable or non-absorbable and placed inside or outside the meniscus.
- If the decision is made to remove the damaged part of the meniscus, the surgeon will use surgical instruments to trim the torn edges and remove the damaged portion only.
- Once the repair or removal is complete, the surgeon will close the incisions with sutures and cover them with a dressing. The knee may also be wrapped in a compression bandage for 24 hours to help control swelling.
After the Procedure
- The patient will be monitored in the recovery room until they are alert and able to move the knee.
- Pain medication and antibiotics may be prescribed to manage pain and prevent infection.
- The patient will be advised to rest, ice the knee, and keep it elevated for the first few days after the surgery.
- Physical therapy may be recommended to help regain strength and mobility in the knee.
Post-op Instructions
Rest and Ice
Rest your knee as much as possible for the first few days after surgery. Apply ice to the area for 20-30 minutes every 2-3 hours to help reduce pain and swelling.
Pain Management
Take any pain medications as prescribed by your doctor. If you experience any allergic reactions, contact your doctor immediately.
Dressing Care
Keep your dressing and incision site clean and dry. Follow your surgeon's instructions for changing the dressing.
Mobility and Weight-bearing
Use crutches as directed by your surgeon. Weight-bearing is allowed as tolerated.
If the meniscus is repaired, you will be placed in a Hinge knee brace set in full extension up to 90 degrees of flexion for six weeks. This range of motion reduces the stress over a recently repaired meniscus. If the debridement is only performed and no meniscus is repaired, the hinge knee brace is not recommended.
Physical Therapy
Attend physical therapy sessions as your doctor recommends to help restore your knee's strength and mobility.
Follow-up Appointments
Attend all follow-up appointments with your surgeon to ensure proper healing and to monitor your progress.
Avoid Certain Activities
Avoid any activities that stress your knee, such as running, jumping, or twisting, until your doctor instructs you.
Nutrition
Eating a healthy, well-balanced diet can help promote healing.
Communicate with Your Doctor
If you have any concerns or questions about your recovery or if you experience any unusual symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
It is important to follow these instructions carefully to ensure a smooth and successful recovery from knee meniscus repair surgery.
Knee Meniscus Repair Prognosis
The prognosis for knee meniscus repair depends on several factors, including the extent of the damage, the patient's overall health, compliance with postoperative rehabilitation, and the location of the tear and tear chronicity. Most patients can expect to return to normal light activities within four to six weeks after the surgery, although strenuous activities may need to be avoided for up to 3 months.
In general, knee meniscus repair has a high success rate and can provide long-term relief from pain and improved knee function. However, there is always a risk of complications, such as infection, bleeding, nerve damage and failure of the meniscus to heal. Despite optimal surgical technique, we still rely on patients' biology and ability to heal the tear.
Knee Meniscus Repair Risks
Like any surgical procedure, knee meniscus repair carries a risk of complications. Some of the most common risks include:
- Infection: Although rare, infections can occur in the knee after surgery and may require additional treatment.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after the surgery may require additional procedures or blood transfusions.
- Nerve damage: The surgical instruments used during the procedure may damage nearby nerves, leading to numbness or weakness in the knee or leg.
- Blood clots: Patients may be at an increased risk of developing blood clots in the leg after the surgery, which can be dangerous if they travel to the lungs.
What if Knee Meniscus Repair is Delayed?
Delaying knee meniscus repair can lead to worsening symptoms and an increased risk of complications. If left untreated, a torn meniscus can cause arthritis, chronic pain, and limited mobility in the knee joint. In some cases, delayed treatment may make it more difficult to repair the meniscus, which could require a more invasive procedure or even knee replacement.